The Specific Allergies Venom Immunotherapy Can Treat
Approximately 7% of the US population is at risk for a severe reaction to their next stinging insect sting.4 Hymenoptera venom allergies are also one of the most common causes of allergies in adults. But don’t worry, venom immunotherapy can treat allergies to stings from: Depending on your allergies, you may receive allergy shots containing insect-specific venom or mixed doses that treat several stinging insect allergies. Your medical provider can run tests and provide you with the best treatment options for you.Receiving Treatment
Most likely, you will receive allergy shots in a doctor’s office. The medical provider will inject a minimal amount of venom diluted in saline under your skin. After receiving the shot, the staff will ask you to stay in the office for a short time. This way, if you have a severe reaction to the venom, you can receive prompt medical care. Due to the minimal amount of venom injected, a severe reaction is rare, however. Instead, you are more likely to experience redness and warmth at the injection site. These symptoms will diminish after a short time. Other symptoms include hives, itching, and swelling near the shot.
After being diagnosed with a bee or wasp allergy, you can pretty much start on venom immunotherapy as soon as can be arranged. If there are no insurance restrictions, this can mean within days of being tested and having the diagnosis confirmed.
Dr. Steven Kernerman
ONGOING TREATMENT
Venom immunotherapy is an ongoing treatment. At first, you will receive one shot per week for a month. These doses will also be minimal and slowly increase. Your body needs time to acclimate to the venom.10
After this initial period passes, you most likely can begin to receive shots once per month. At this point, you will have worked your way up to full-dosage shots, also called the maintenance dose. 97% of patients show no systemic reaction 2.5 – 3.5 months into treatment while receiving the maintenance dosage.10
Then, during your first couple years of treatment, your
maintenance doses will gradually become less frequent: every four weeks, to
every eight weeks, and eventually, perhaps even 12 weeks apart. Studies suggest
that treatment can be stopped after three to five years, depending on age and
severity.12
Bee sting allergies are serious
Discover how venom is collected for immunotherapy.
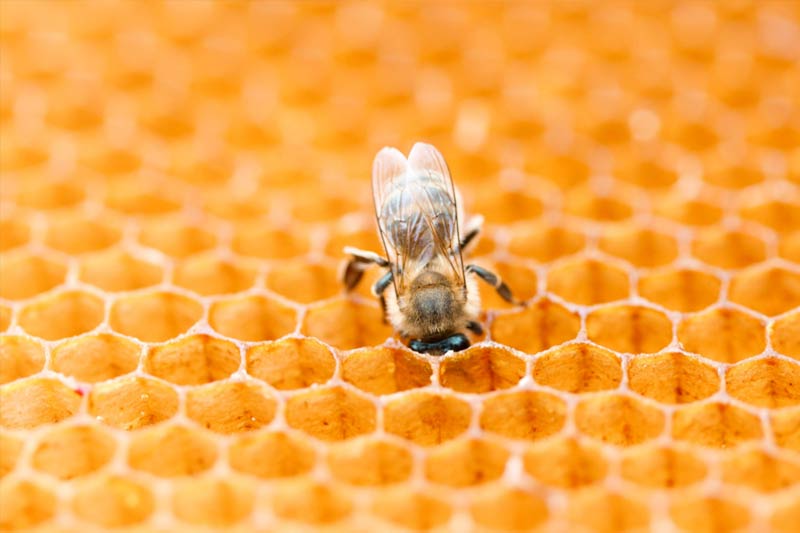

In contrast to honey bees, venom sacs from other stinging insects must be hand-dissected with tweezers. Each sac is only the size of a pinhead, making the process tedious and difficult. In fact, it takes 520 staff-hours to collect the 130,000 sacs needed for one batch of product for immunotherapy.
DOES IT WORK?
YES! Venom immunotherapy is up to 98% effective in preventing systemic allergic reactions to bee stings.3 If you or a loved one suffer from severe allergies, this treatment may be worth the weekly and monthly appointments. As treatment progresses, the anxiety of being outdoors slips away—even if an epinephrine pen isn’t in reach.
Hear a family's success story.
Learn how an avid gardener continued her passion with immunotherapy.

Katherine K. Schlosser is an author and lecturer on native plants and herbs. Despite her allergy to honeybees, wasps, hornets, and yellow jackets, she spends most of her professional and personal life outdoors.
OTHER ARTICLES ABOUT VENOM IMMUNOTHERAPY
Go more in-depth with these articles on venom immunotherapy:
KNOWING IF VENOM IMMUNOTHERAPY IS RIGHT FOR YOU
Venom immunotherapy isn’t right for everyone. For instance, young children under the age of 5 are not often candidates due to their inability to communicate symptoms. There may also be other health factors that prevent you from this type of treatment.
The best way to find out if venom immunotherapy is right for you is to talk to a medical provider in your area.


Find a Local Allergist
If you think you have a bee sting allergy, don’t wait for an emergency. Instead, talk to an allergist about testing and venom immunotherapy.





